Pauline Harding, MD, Family Medicine Practitioner
One young adult male from out-of-state had resolutions of his longstanding intestinal bleeding upon identifying gluten as the cause of his bowel disease. Two colonoscopies had not identified the issue.
The digestive tract is much more than simply a food processing system. The gut plays an important role in the interaction between diet and immunity. It is the largest contact area with the environment, larger than the skin or respiratory system. If spread out on a flat surface it would be about the same size as a tennis court, with the doubles lanes included.
Likewise, the nutritional requirements of the body are substantial and here too the gut plays a central role. A poorly functioning gut can not only be uncomfortable it can also have serious impact on physiological function.
Common GI disorders include bloating, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diarrhea, heartburn, reflux, constipation, nausea and others; like, celiac disease and Crohn’s disease, often times such problems are of unknown origin and resist treatment. However, the cause in many cases may be improved or even resolve by modification of diet. It is now well understood that gluten containing grains cause the spaces between the intestinal cells (the tight junctions) to open. When this occurs the natural gut barrier to undigested foods, as well as toxins and gut microbes is compromised (this is referred to as “leaky gut”) 1. Moreover, white blood cells can interact with the gut contents which can lead to local inflammation, swelling, or irritation in the intestines 2. This condition usually resolves when the food triggers are eliminated from the diet.
The Alcat Test may be an effective way to identify offending foods and other ingestions (herbs, functional foods, additives, colorings, etc.) that act as triggers of the above mentioned problems. Likewise, the Gut Health Protocol (GHP) offers useful information enabling important steps toward symptom resolution, especially if underlying non-celiac gluten sensitivity and inflammatory conditions such as Crohns’ disease are suspected.
Validation studies are presented below.
IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), Stomach discomfort
03/01/2013
Thank you Alcat! My experience could not have been more positive from the very beginning.
The Alcat Test staff were incredibly helpful during my research and testing phase. I was experiencing itchy skin and stomach aches on a nearly daily basis, as well headaches and irritable bowel symptoms far too regularly.
I am 30 years old. I get exercise, didn’t have weight to lose, I eat a healthy diet and I was already avoiding known food allergies so I was frustrated and didn’t know what was going on. The day I received my results I eliminated my reactive foods from my diet (shocking results to me: blueberries, artichoke, cranberries and more, food I love and ate regularly). I have not had a single stomach ache, headache, or irritable bowel symptom since that day 4 weeks ago! My itchy skin is almost gone. I feel better than I have in years. People tell me I look great. And the most exciting part is knowing that these foods aren’t gone forever; I’ll probably be able to eat most of them without symptoms recurring by following the recommended rotation diet. I am a firm believer and highly recommend the Alcat Test to family, friends, anyone!
Corrin from Washington
03/01/2013
I just wanted to take a few minutes to just say thank-you.
The combination of the Alcat Test and your expertise has given me just the answers I looked for and a plan of action to get my IBS symptoms under control. I have seen many so called specialists, who offered Prescription Drugs, with numerous possible side effects, all to no avail.
Carlos from Nevada, Captain Major US Airline
IBS is a multi-factorial, functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by complex pathophysiology and unspecific symptoms. It is one of the most common intestinal disorders associated with abdominal pain, cramping or bloating, diarrhea or constipation. IBS is a chronic condition that presents with varying and intermittent symptom severity. Most people’s symptoms are sufficiently mild that they never seek medical care. However, some people may have troublesome symptoms, especially abdominal cramps, bloating, heartburn, and diarrhea combined with other problems accompanied by companion symptoms, including, migraine, chronic fatigue syndrome or fibromyalgia 3. The cause of IBS is not well understood. However, it is widely accepted that it involves dysfunction of the gut microbiome and immune response 4.
With IBS digestive function is impaired, but there may be no direct evidence of organic damage. Other parameters such as blood levels of liver and pancreas enzymes in blood and stool samples are within normal ranges; and, stomach and colonoscopy may show no abnormal findings. Nonetheless, the discomfort, un-wellness or limitations of such functional disorders are a reality.
Changes in diet and lifestyle; avoiding certain trigger foods and managing stress, may offer significant benefit. However, one should never assume that diet change alone is a substitute for appropriate medical care from a qualified practitioner.
Celiac disease vs. Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS) Link to GHP (detailed info)
Celiac disease and NCGS underlie two completely different immune activation pathways – celiac disease, an auto-immune disease, wherein the immune system attacks its own tissue – in this case the intestinal villi – is a reaction of the specific immune system. NCGS, on the other hand, appears to be a function of the nonspecific branch of the immune system 5.
People affected by celiac disease may have to permanently eliminate gluten-containing grains (e.g. wheat, rye, barley, spelt etc.) otherwise serious damage to the intestinal lining, and malnutrition, will ensue. It should be noted that hundreds of prepared foods, soups, sauces, snacks, etc. may contain gluten. Of course, in all instances where major food groups are avoided it is wise to involve the counsel of qualified professionals.
NCGS, on the other hand is not necessarily genetically based. Therefore, gluten-sensitive people may, or may not, be able to tolerate gluten containing grains after an elimination period of 3-6 months. This can be determined by experimenting with reintroduction of the food(s) or by retesting.
The gliadin fraction in gluten (protein complex) can cause an increased expression of zonulin 6. Zonulin is a protein that regulates the permeability of the intestine that is the opening of the “contact zones” (tight junctions) between the intestinal cells, thus causing the condition now termed, “leaky gut”. This function is most important for example to flush invaders such as bacteria, virus or parasites. However, if this mechanism is triggered inappropriately through the unnatural or excessive intake of gluten products, gut permeability can become chronic.6. Onset of this inflammatory response typically takes one to two days to occur but can last for several days.
The non-specific immune response seen in gluten sensitivity may manifest in the gastro-intestinal tract, but also through the skin, weight gain, Diabetes, headache, joint pain, respiratory symptoms and others.
The Alcat Test is designed to identify cellular reactions to gluten containing grains as well as grains not containing gluten/gliadin as well as other food triggers The Gut Health Profile, or GHP, can help determine a genetic disposition to celiac as well as disease progression, the likelihood of Crohn’s being present, or ruling out the probability of these diseases.
Test recommendations for gastrointestinal conditions
| What test? | Why? |
|
Alcat Test for food intolerance & chemical sensitivity
PreviMedica Program LINKs
|
Validation studies show that dietary modification based upon Alcat Test results can have very positive effects on gastrointestinal disorders:
|
| Gut Health Profile (GHP)
LINK to GHP |
|
| Adrenal Stress Profile | Stress can compromise gut function.
|
| Vitamin D |
|
Effectiveness and validation of the Alcat Test
Beginning in 1988, and carrying through to the present, several clinical studies have been performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the Alcat Test. Some of which were “double-blinded*” to see how well the test results correlate with actually eating the food.
A valid test for food intolerance should show the effect of food substances on those cells of the immune system which are associated with the inflammatory process.
(Note to us: it would be good to link to references that link neutrophil activation to certain disease conditions, LINK to Alcat Test immunology section?).
If the test results are valid there should be in a concordance with symptoms (e.g., gastrointestinal complaints), and correlate with double blind oral exposure.
(*Double-blind studies: To obtain an unbiased outcome the study must be carried out in double blind fashion wherein neither the doctor (investigator) nor test subject knows whether the food they are re-introducing has been indicated by the blood test as being either positive or negative. The test results are evaluated to see if they correlate with this, the, “gold standard” – a double blind oral challenge. This is a rigorous and time consuming protocol that yields an objective evaluation of both the sensitivity and the specificity of the test.)
Why is that important?
This is important because you want the test to correctly identify reaction provoking substances; but, you also do not want the test to show false positives. The first parameter is called, “sensitivity”. The second is called, “specificity”. A false positive would cause you to needlessly eliminate a safe food.
Scientists have shown that in patients with irritable bowel syndrome, atopic eczema, allergic rhinitis or migraine the Alcat Test can detect those foods that cause the above symptoms. The Alcat Test has shown high correlation with double-blind oral challenges: 83.4% with foods and 96% with food additives.
Link studies
- High Correlation of the Alcat Test Results with Double-blind Challenge (DBC) in Food Sensitivity (P. Fell, Bostoff et al, 1988 and published in the Annals of Allergy)
- Diagnostic Value of Alcat Test in intolerance to food additives compared with double-blind placebo-controlled (DBPC) oral challenges ( Hoj, J Allerg Clin Immun 1 (3); 1996)
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 14-16
Reproducibility of the Alcat Test
Drs. P. Potter and H. Steinmann of the University of Cape Town, South Africa conducted an Alcat Test reproducibility study in 1994. The study found high reproducibility (95%) of both positive and negative test results. . Reproducibility of the Antigen Leukocyte Cellular Antibody test (Alcat) – Statistical Analysis, Summary Statistics & Scientific Report
A second Alcat reproducibility study was conducted at the University in Bloemfontein, South Africa by Dr. WML Neetling and Dr. AM Kachelhoffer, January to April, 1998.
The study analyzed 10 consecutive patients. Of these, 2 patients had no prior allergies. The balance reported various symptoms such as migraine, asthma, and IBS. Using the Alcat Test, 1,300 analyses of 4,989 data points were performed, testing responses to 130 antigens. The study demonstrated 92% reproducibility.
Parexel Medstat Final Statistic Report
Study of the Alcat Test in 10 subjects tested twice: 1000 data points:
- Reproducibility: 97% in Cohort A, 99% in Cohort B. Overall,
- 983 of 1,000 Alcat Test data points (98.3%) were reproducible under the conditions investigated by the study. The study demonstrated the statistically significant reproducibility of the Alcat Test results.
- Study comparing the Alcat Test results with flow cytometry and microscopy. Gitte Jensen, NIS Labs (Natural Immune System) Oregon, USA, 2009
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 17 No 1-4
Studies of the Alcat Test and its use with gastrointestinal disorders
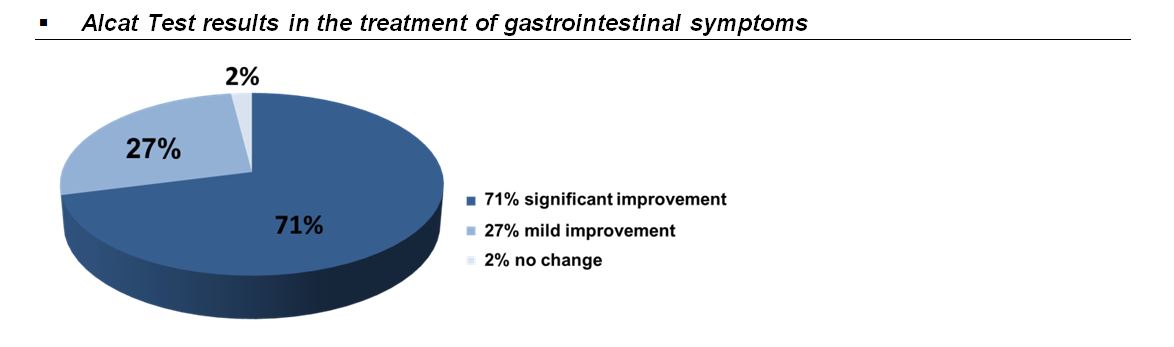
Investigators Berardi L, De Amici M, Castello C, Torre, Giunta, Legoratto, and Vignini studied 48 patients who participated in an elimination diet based on Alcat Test results. They found that the Alcat Test-based diet improved symptoms in 71% of patients. In particular, symptom improvements were most evident in patients with higher symptom scores, dietary changes and everyday conditions. Presented at 30th Congress of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 11-15 June 2011 – Istanbul, Turkey, and published in Allergy Volume 66, Supplement s94, June 2011 – pg. 63, abstract 552.
More details: Scientific Dossier p. 18, No 2
Alcat Test identifies food intolerance in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms
Investigators Berardi L, De Amici M, Vignini, Mantegna, and Mosca conducted a study with a group of 15 patients (4 males and 11 females) affected by GI symptoms and negative for allergies (prick and/or rast); the participants agreed to be tested with the Alcat Test. They concluded that 54% of the test subjects’ symptoms improved significantly. Presented at 28th Congress of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 6-10 June 2009 – Warsaw, Poland, and published in Allergy Volume 64, Supplement 90, 2009 – pg. 490, abstract 1280.
More details: Scientific Dossier p. 18, No 4
Gastrointestinal Complaints related to diet
Douglas H. Sandberg MD reported that in patients following an Alcat based elimination plan was an effective method in alleviating symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders. Published in International Pediatrics Volume 5, Number 1, 1990.
More details: Scientific Dossier p. 23 No 20
Cellular Responses to Food in Irritable Bowel Syndrome – An Investigation of the Alcat Test
Investigators Fell PJ, Soulsby S, and Brostoff J conducted a double blind, placebo controlled study on 20 patients which demonstrated that an Alcat Test based elimination diet dramatically improved symptoms of IBS and had a statistically significant correlation between an Alcat score and symptom provocation. Published in Journal of Nutritional Medicine, Volume 2, Number 2, 1991.
More details: Scientific Dossier p. 16 No 4
El test Alcat de Sensibilidad a los Alimentos y su Interés en Medicina Estética
Investigator Cabo-Soler et al. at the 14th Med Day of Aesthetic Medicine & Dermatology, Venice, Italy, September 22-23, 1995 and published in Estetica Medica Numero 40 – March 1996 (Spanish).
Summary: This study considered 30 patients who previously had difficulty losing weight even though
they followed calorie restrictive diets. Weight loss and body composition were compared at 4 weeks following a conventional calorie restrictive diet compared with Alcat Test results. Nearly all patients lost more weight following the Alcat-based calorie restrictive diet. Furthermore, most patients lost fat and gained muscle mass on the Alcat prescribed diet. In addition, the patients following Alcat informed diets reported feeling better and having improved energy. Digestive disorders (e.g., bloating and indigestion). Skin problems also improved.
More details: Scientific Dossier p. 19 No 10
Outcome study in 353 consecutive patients following the Alcat Diet
Observational study conducted in Copenhagen at the Allergy Clinic Charlottenlund, Denmark (1996, unpublished)
Dr. Geldenhuys, 1997 in Johannesburg, described data collected from his patients treated with diets based upon their Alcat Test results.
This randomized study followed 274 patients with different symptoms who adhered to a diet plan based on their individual Alcat Test results. The percentage of patients that experienced improvement or complete recovery from their health complaints was as follows:
- 78% Migraine
- 77% Arthritis
- 67% Eczema
- 71% Intestinal cramps
- 71% Chronic fatigue
- 73% Diarrhea/constipation
- 62% Chronic sinusitis
More detail: Scientific Dossier, p. 24, Nr. 21
Alcat Test Results In The Treatment of Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Symptoms, Arthritis, Skin and Central Nervous System
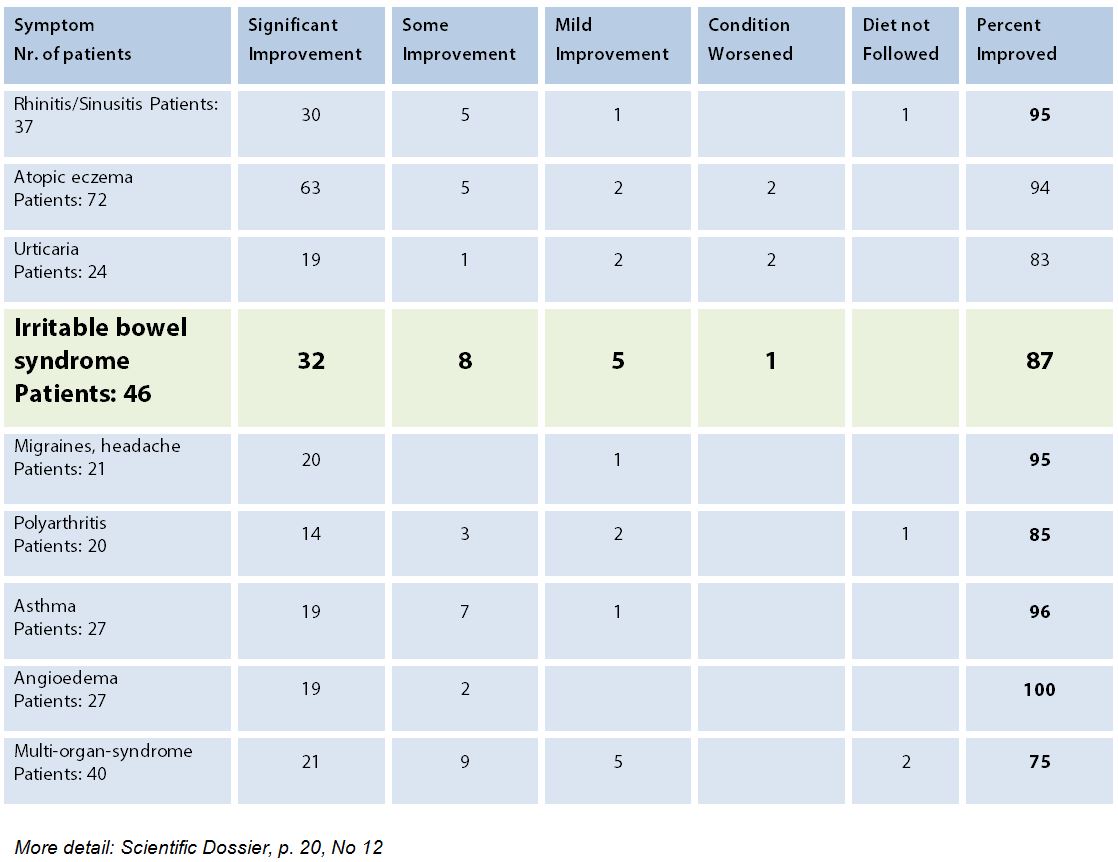
Investigator Mylek D studied 72 patients who followed an Alcat based elimination diet; they had significant improvement in their symptoms that included arthritis, bronchitis and gastro issues. Specifically, they found improvement in 83% of arthritis patients, 75% of Urticaria, bronchitis, and gastroenteritis patients, 70% of migraine patients, 60% of chronic fatigue syndrome patients, 50% of asthma patients, 49% of AD patients, 47% of rhinitis patients and 32% of hyperactivity patients. Patients were also skin tested for IgE allergy to inhalants and foods that were more pronounced in skin and nasal symptoms. Published in Advances in Medical Sciences; Formerly Roczniki Akademii Medycznej w Bia?ymstoku Volume 40, Number 3, 1995.
More detail: Scientific Dossier, p. 20, No 13
The Alcat Test – A Guide and Barometer in the Therapy of Environmental and Food Sensitivities
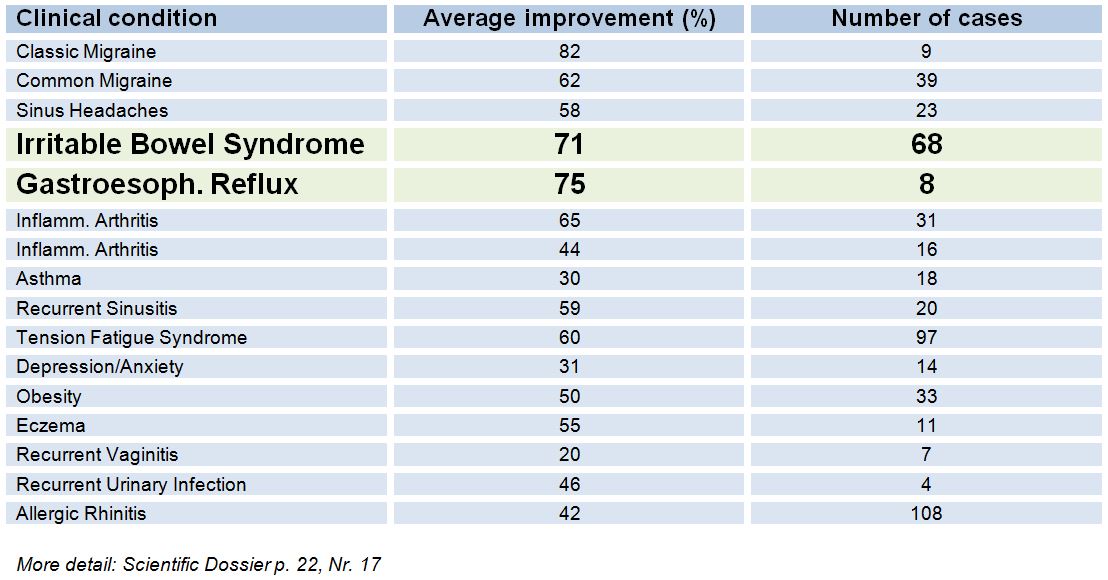
Investigator Solomon BA studied 172 patients successfully using an Alcat Test based diet to alleviate the following range of symptoms: classic migraine (85%), common migraine (62%), sinus headaches (58%), gastoesphageal reflux (GERD) (75%), IBS (71%), inflammatory arthritis (65%), recurrent Sinusitis (59%), tension fatigue, syndrome (60%), obesity (50%), eczema (55%), asthma (30%), depression and/or anxiety (31%), recurrent vaginitis (20%), recurrent urinary tract infection (46%), degenerative arthritis (44%) and allergic rhinitis (42%). Environmental Medicine, Volume 9, Number 1 & 2, 1992.
More detail: Scientific Dossier, p. 22, No 17
The Alcat Test – A Guide and Barometer in the Therapy of Environmental and Food Sensitivities
172 patients (Dr. BA Solomon, Environmental Medicine, Vol. 9, Number 2, 1992:2-6).
Literature
1 Fasano A. Zonulin and its regulation of intestinal barrier function: the biological door to inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):151-75.
2 Fournier BM and Parkos CA. The role of neutrophils during intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunology (2012) 5, 354–366.
3 Hulisz D. The burden of illness of irritable bowel syndrome: current challenges and hope for the future. J Manag Care Pharm. 2004 Jul-Aug;10(4):299-309.
4 Konig J, Brummer RJ. Alteration of the intestinal microbiota as a cause of and a potential therapeutic option in irritable bowel syndrome. Benef Microbes. 2014;5(3):247-61.
5 Sapone A et al.: Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Med, 2011.9:p.23.
6 Fasano F: Leaky Gut and autoimmune disease. 2012