02/14/2013
MLB Outfielder took the Alcat Test and visited the Cell Science Systems Laboratory.
“I took the test and immediately told myself that if this is right and this is right for me I will do this by the book. I had a severe reaction to hazelnut and then some moderate reactions to some other foods, cut those foods out, cut all sugar out for a month and immediately lost thirty five pounds.”
Cliff Floyd
“I am 6-weeks into the elimination and rotation diet and the results have been nothing short of a miracle! I have lost 13 pounds, my skin is clearing up, I sleep well, digest well, feel strong and have a lot of energy. I realize now that I have had food intolerances all of my adult life – I am only sorry that it has taken this many years to finally get to the cause of my health problems. If I had only known that good health was really so simple to achieve. Thank you, Alcat!”
Laura from Kansas
03/01/2013
“At 220 pounds I had been diagnosed with Osteoarthritis, Adult Onset Asthma, and High Blood Pressure. I was Border Line Diabetic and had Pitted Edema in my legs to the extent I wore support hose for 5.
My ailments were only out numbered by the medications I took for them. I started trying to lose weight.
Without much support or direction, I tried several nationally advertised well known diet plans. I would lose a little and gain even more. After approximately 3 years of this yo-yo I had gained an additional 32 pounds, and was now at my top weight of 252 pounds. Then I found the Alcat Test through a book I was reading. Unlike the “diet plans” I had seen before, the Alcat Test spoke of food sensitivity and a medical reason why my body was not responding to a healthy diet.
After taking the Alcat Test, I found my most severe food sensitivities were some of the healthiest foods I ate, and I ate them on a daily basis. (Lettuce, tomatoes, green peppers, onions, and lemons, to name a few). When I started the Alcat Test rotation diet I was sure this was something that could change my life. When I eliminated the foods I was intolerant to I started losing weight almost immediately, an amazing 15 pounds the first 2 weeks. In the following 11 weeks I lost an additional 70 pounds. After approximately 10 days I was able to stop taking all six prescription medications. I lost an incredible 16 inches on my waist line; and went from a 3XL shirt to a medium.
The Alcat Test is absolutely amazing.”
Joe from Fort Lauderdale, FL
Metabolic Conditions
Inflammatory signals play a role in all metabolic disorders. They mediate the immune response and the activation of the innate immune system. Neutrophils (the main group of white blood cells) secrete their biochemical contents to fight damaging particles, after which they perish scavenger cells (phagocytes) eat the cell debris for removal. If this is an ongoing process a lot of energy is directed into the immune system.
The Alcat Test helps to identify dietary triggers of Inflammation.
Weight Gain and Obesity
It’s true that we gain weight when we eat more than we burn off. Many factors can impact the , “burning off” part of the equation. Chronic inflammation is one of them.
Weight gain can also be caused by hypothyroidism, food sensitivity (as mentioned) Cushing’s syndrome, organ disease, prescription drug use (e.g. antidepressants) anxiety, blood sugar imbalance, essential fatty acid deficiency or lack of sleep. Many people respond to stress or depression by eating excessively. Reactions to foods are not always immediate. They may be delayed by several hours, possibly even one or two days. Common signs include;bloating and swelling in the hands, feet, ankles, abdomen, skin and around the eyes. Much of the weight gained is fluid retention caused by inflammation and the release of certain hormones. In addition, there is fermentation of foods, particularly carbohydrates, in the intestines which can result in a swollen distended belly and gas production. Inflammation associated with food sensitivities can lead to weight gain and obesity 1, 2.
According to the WHO a BMI (body mass index) equal to or more than 25 is considered overweight. A BMI equal to or more than 30 is considered obese 3. Obesity can lead to pathological, chronic disorders like diabetes, cardiovascular conditions and cancer 3. The WHO suggests that in 2008 more than 1.4 billion adults were overweight and of these over 200 million adults were obese 3. Obesity is a preventable condition according to the WHO.
…Healthy weight loss!
The inability to achieve and maintain a healthy weight might be silent inflammation (chronic low-level inflammation) 4. BMI is based only on the size in relation to weight, but does not consider the real “body composition”, including abdominal or peripheral fat accumulation (fat around organs). Hence, measurement of BMI without measurement of body composition, may be misleading. It is possible to not be overweight but to be over fat.
What causes overweight?
How much does the lean, fat-free body part weigh, and how much does the fat? A person can be overweight without a high body fat percentage. The overweight may come from muscle mass. When it is placed in relation to the fat percentage, muscle mass is denser and therefore weighs more. A person who is not “fat-overweight” is not under the same disease risks, such as a “fat-overweight”. On the other hand, people may have a too high fat content but “ideal weight” according to the BMI. This condition is called normal weight obesity. Consequently, the risk of disease and inflammation is higher, even though they fall within the ideal weight category.
Thus the fat proportion plays the biggest health role, regardless of the weight. Too much muscle mass pose no health risks. In contrast to the widespread opinion that fat is stored in the form of a wobbly mass as excess calories, it is metabolically active tissue 5. Leptins are hormones which are produced in fat cells 5. They send signals to the brain that you are sated. But if excessive fat is accumulated – particularly in the abdominal and peripheral area – adipose tissue then becomes an important endocrine tissue and sends inflammatory biochemicals 5. These inflammatory mediators cause low grade systemic inflammation in “fat-obese” people even though weight is normal according to the BMI!
Several studies of the Alcat Test show characteristic weight loss going along with the Alcat program. A study performed with 27 obese patients shows an average weight loss from 91.37 ± 10.56 kg to 74.6 ± 6.76 kg after following the Alcat Test results and rotational diet for 12 weeks (Akmal et al., 2009- find below).
The Alcat Test program provides an excellent basis for a sustainable weight loss and weight management. The program enables a diet that helps to prevent unwanted cellular defense responses to food particles. The Alcat Test is not a diet, but is a basis for enabling intelligent and profound dietary modification.
Metabolic Syndrome
Also known as Reavan syndrome or Syndrome X, the Metabolic syndrome is not a disease but combines multiple symptoms: obesity, fat metabolic disorder (dyslipidemia), elevated blood pressure, and insulin resistance. It is also associated with several additional conditions like sleep apnea, male hypogonadism and polycystic ovary syndrome 6. The widely accepted cause of the metabolic syndrome is diet and lifestyle related. . It starts with overweight or obesity which leads to insulin resistance. Insulin in turn controls blood sugar levels. High levels of insulin may cause insulin resistence and later, type II diabetes. (The inflammatory mediators produced by immune cells, particularly, TNF alpha and IL-6, are known to block insulin receptors.)
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a group of chronic metabolic disorders, which can cause severe long-term conditions such as cardiovascular disease (heart disease and stroke) and kidney failure 7, 8. Diabetes is of two types: type I diabetes (decreased production of insulin), type II diabetes (insulin resistance) and gestational diabetes (pregnant women with high blood glucose levels) 9. In all cases, the blood sugar level can no longer be solely regulated by the body and is therefore abnormally increased. It is estimated that approximately 347 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes 9.
Arthritis urica, gout
Link to musculoskeletal – gout
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and conditions
Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is a condition in which plaque builds up inside the arteries with local inflammatory processes 10. Consequently the arteries become clogged, which limits the transport of oxygen-containing blood to the organs. It can lead to CVD. e.g. heart attack and stroke. The plaque can consist of fat, cholesterol and other components in the bloodInflammation plays a major role in turning cholesterol into plaque.
Cardiovascular diseases
CVD includes pathologic conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels like coronary and rheumatic heart disease or peripheral arterial disease and deep vein thrombosis (blood clots) 11. CVDs represent the number one cause of death worldwide 11, 12. Main risk factors include unhealthy diet, lack of physical exercise, smoking, and excessive use of alcohol 11.
Test recommendations for weight management, metabolic and cardiovascular conditions
| What test? |
Why? |
|
Alcat Test for food intolerance & chemical sensitivity
PreviMedica Program LINKs
|
Validation studies show that the Alcat Test can have very positive effects on gastrointestinal disorders:
|
| MTHFR
Methyltetrahydrofolate Reductase Genetic Mutations |
|
| Adrenal Stress Profile | Stress can cause inflammation and thus cause IBS.
|
| Telomere length test |
|
| Vitamin D |
|
Effectiveness and validation of the Alcat Test
Beginning in 1988, and carrying through to the present, several clinical studies have been performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the Alcat Test. Some of which were “double-blinded*” to see how well the test results correlate with actually eating the food.
A valid test for food intolerance should show the effect of food substances on those cells of the immune system which are associated with the inflammatory process.
(Note to us: it would be good to link to references that link neutrophil activation to certain disease conditions, LINK to Alcat Test immunology section?).
If the test results are valid there should be in a concordance with symptoms (e.g., gastrointestinal complaints), and correlate with double blind oral exposure.
(*Double-blind studies: To obtain an unbiased outcome the study must be carried out in double blind fashion wherein neither the doctor (investigator) nor test subject knows whether the food they are re-introducing has been indicated by the blood test as being either positive or negative. The test results are evaluated to see if they correlate with this, the, “gold standard” – a double blind oral challenge. This is a rigorous and time consuming protocol that yields an objective evaluation of both the sensitivity and the specificity of the test.)
Why is that important?
This is important because you want the test to correctly identify reaction provoking substances; but, you also do not want the test to show false positives. The first parameter is called, “sensitivity”. The second is called, “specificity”. A false positive would cause you to needlessly eliminate a safe food.
Scientists have shown that in patients with irritable bowel syndrome, atopic eczema, allergic rhinitis or migraine the Alcat Test can detect those foods that cause the above symptoms. The Alcat Test has shown high correlation with double-blind oral challenges: 83.4% with foods and 96% with food additives.
Link studies
- High Correlation of the Alcat Test Results with Double-blind Challenge (DBC) in Food Sensitivity (P. Fell, Bostoff et al, 1988 and published in the Annals of Allergy)
- Diagnostic Value of Alcat Test in intolerance to food additives compared with double-blind placebo-controlled (DBPC) oral challenges ( Hoj, J Allerg Clin Immun 1 (3); 1996)
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 14-16
Reproducibility of the Alcat Test
Drs. P. Potter and H. Steinmann of the University of Cape Town, South Africa conducted an Alcat Test reproducibility study in 1994. The study found high reproducibility (95%) of both positive and negative test results. . Reproducibility of the Antigen Leukocyte Cellular Antibody test (Alcat) – Statistical Analysis, Summary Statistics & Scientific Report
A second Alcat reproducibility study was conducted at the University in Bloemfontein, South Africa by Dr. WML Neetling and Dr. AM Kachelhoffer, January to April, 1998.
The study analyzed 10 consecutive patients. Of these, 2 patients had no prior allergies. The balance reported various symptoms such as migraine, asthma, and IBS. Using the Alcat Test, 1,300 analyses of 4,989 data points were performed, testing responses to 130 antigens. The study demonstrated 92% reproducibility.
Parexel Medstat Final Statistic Report
Study of the Alcat Test in 10 subjects tested twice: 1000 data points:
- Reproducibility: 97% in Cohort A, 99% in Cohort B. Overall,
- 983 of 1,000 Alcat Test data points (98.3%) were reproducible under the conditions investigated by the study. The study demonstrated the statistically significant reproducibility of the Alcat Test results.
Study comparing the Alcat Test results with flow cytometry and microscopy. Gitte Jensen, NIS Labs (Natural Immune System) Oregon, USA, 2009
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 17 No 1-4
Studies of the Alcat Test and its use with weight management, metabolic and cardiovascular disorders
- The Short Term Efficacy of the Alcat Test of Food Sensitivities to Facilitate Changes in Body Composition and Self-Reported Disease Symptoms: A Randomized Controlled Study
Investigators Kaats GR, Pullin D, Parker LK. The patients’ group following the Alcat Test Plan LOST SIGNIFICANTLY (p<.001) MORE SCALE WEIGHT, % BODY FAT and FAT WEIGHT; had GREATER IMPROVEMENTS in BODY COMPOSITION (p<.001) and had GREATER INCREASES IN FAT-FREE MASS (p<.001). When compared to the control group, the Alcat group reported improvements in ALL 20 items on a Disease Symptom Inventory Self Report. It was concluded that, as compared to participants following a weight control plan of their own choosing, following the Alcat test and diet plan resulted in HIGHLY SIGNIFICANT IMPROVEMENTS IN BODY COMPOSITION AND SELF-REPORTED DISEASE SYMPTOMS. 80% of the Alcatgroup lowered their body fat and 78% achieved an improvement in body composition. Published in American Journal of Bariatric Medicine, spring 1996.
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 19, Nr. 9
- The Effect of The Alcat Test Diet Therapy for Food Sensitivity in Patient’s With Obesity
Investigators Mohammed Akmal, Saeed Ahmed Khan, and Abdul Qayyum Khan studied 27 obese patients who were not successful losing weight following a low calorie diet and then placed the patients on an ALCAT based elimination diet. Twelve weeks following the diet, the patients lost a statistically significant amount of weight and fat. In addition, they experienced an overall improvement in well-being. Published in Middle East Journal of Family Medicine, April 2009, Volume 7, Issue 3
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 18, Nr. 6
- The Alcat Test – A Guide and Barometer in the Therapy of Environmental and Food Sensitivities
172 patients (Dr. BA Solomon, Environmental Medicine, Vol. 9, Number 2, 1992:2-6).
Alcat Test results in the treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms
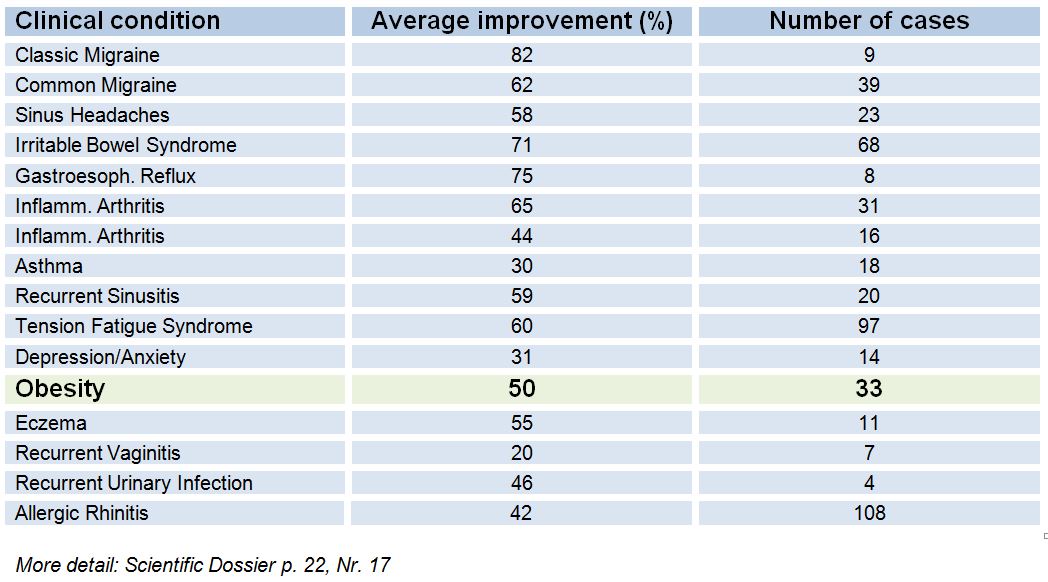
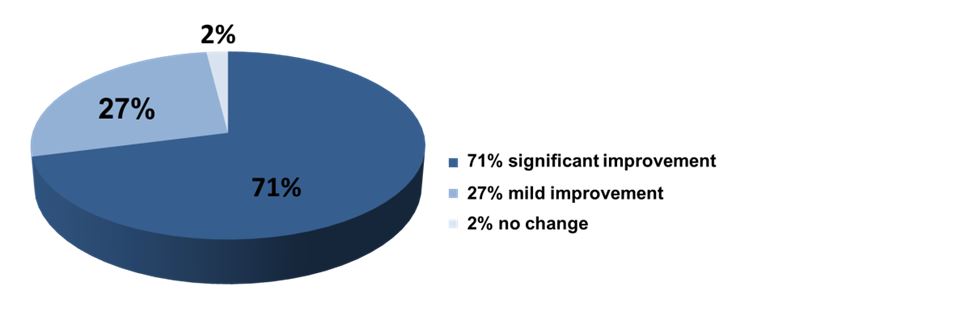
Investigators Berardi L, De Amici M, Castello C, Torre, Giunta, Legoratto, and Vignini studied 48 patients who participated in an elimination diet based on Alcat results. They found that the Alcat Test-based diet improved symptoms in 71% of patients. In particular, symptom improvements were most evident in patients with higher symptom scores, dietary changes and everyday conditions. Presented at 30th Congress of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 11-15 June 2011 – Istanbul, Turkey, and published in Allergy Volume 66, Supplement s94, June 2011 – pg. 63, abstract 552.
More details: Scientific Dossier p. 18, No 2
- Rational management of food intolerance in elite soccer club
Investigators Angelini F, Marzatico F, Stesina G, Stefanini L, Bonuccelli A, Buonocore D studied eight elite (European football) athletes who were selected based on symptoms suspected of being food related. These athletes were placed on an ALCAT based-elimination diet, followed for eight months then retested again. There was significant improvement in the athletes’ condition and reduction in inflammatory response as seem through improvement in body composition. Published in Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition 2011, Volume 8 (Supplement 1).
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 18, Nr. 3
- A Comparison of the Alcat Test for Food Reactions amongst 2 Population Sub-Groups
Investigators Sandberg DH and Pasula MJ concluded the Alcat Test demonstrated a distinct difference in reactivity between a healthy group (25 patients) and a group of 25 patients with food sensitivities. Presented at the 45th Annual Congress of the American College of Allergy and Immunology, Los Angeles, CA: November 12-16, 1988 (published in the Annals of Allergy Congress Preceding).
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 19, Nr. 8
- How to get the best out of a low carb diet
Authors Pescatore and Deutsch; “Journal of Applied Nutrition” (JAN) Voulme 55 (1), 2005 (official publication “International and American Association of Clinica Nutritionists” – IAACN)- combination of carbohydrate-reduced diet and Alcat Test are effective for weight gain.
- El test Alcat de sensibilidad a los alimentos y su interés en Medicina Estética
Author Cabo-Soler et al. Presentation at the „14th Med Day of Esthetical Medicine & Dermatological Survey“, Venice, Italy, Sep. 22-23, 1995 and publicated in “Medica Estetica” Numero 40- March 1996 (spanish). 30 Patients lost weight and body fat after doing the Alcat Test.
More detail: Scientific Dossier p. 19, Nr. 10
Literature
1 Thaler JP, Schwartz MW. Minireview: Inflammation and obesity pathogenesis: the hypothalamus
heats up. Endocrinology. 2010 Sep;151(9):4109-15.
2 Wierucka-Rybak M, Bojanowska E. Bacteria, viruses, and hypothalamic inflammation: potential new
players in obesity. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Mar 12;68:271-9.
3 WHO, Fact sheet N°311, Updated August 2014. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
4 Sears B, and Ricordi C. Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition as a Pharmacological Approach to Treat Obesity
J Obes. 2011; 2011: 431985.
5 Ceddia RB. Direct metabolic regulation in skeletal muscle and fat tissue by leptin: implications for
glucose and fatty acids homeostasis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005 Oct;29(10):1175-83.
6 Cho LW. Metabolic syndrome. Singapore Med J. 2011 Nov;52(11):779-85.
7 Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO
Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia 2001, 44 Suppl 2:S14–S21.
8 Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2011.
9 WHO, Fact sheet N°312, Updated November 2014.
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/
10 Salisbury D, Bronas U. Inflammation and immune system contribution to the etiology of
atherosclerosis: mechanisms and methods of assessment. Nurs Res. 2014 Sep-Oct;63(5):375-85.
11 WHO, Fact sheet N°317, Updated March 2013. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/
12 Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010. Geneva, World Health Organization,
2011.